
Everything You Need To Know About Google Search Ads
Your epic guide to all things PPC!
I will frequently add to and update this page as the industry features and standards evolve. There are no credentials that anyone can really study for in PPC, so we heavily rely on real life experience and testing to learn. We’re opening the doors to you all, on this page we don’t withhold anything, this is a true foundation for Google Search Ads knowledge.
Who should use Google Search Ads?
Search ads work well for any product or service that answers a specific question or need. Yes, that sounds vague, but think about what that means. I’m hungry and I search for “pizza delivery near me”.
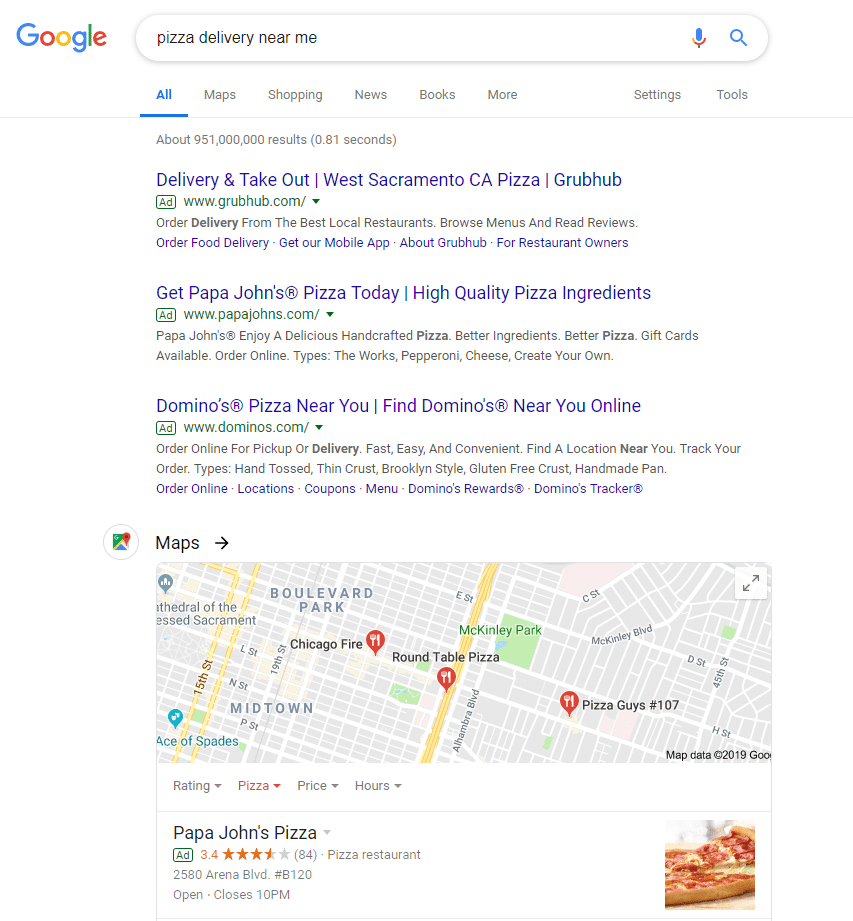
Given these search results, I’m exposed to Papa John’s twice – once in the #2 position in the Search Engine Results Page (SERP), and again with their location extension in the map section.
What the advertiser is doing here is getting in front of searchers with an intent on buying their product or service, rather than traditional advertising that advertises to a broader audience who mostly aren’t interested in the product or service at the time they see the ad.
This applies to all kinds of businesses, like plumbers – if you have a leaking pipe, you’ll Google “plumber near me” and the SERP will present options to the searcher.
NOTICE: All of the results shown above in the screenshot are PAID. Businesses now need to pay to feature anywhere near the top of the search page engine results. This makes it very important to have a healthy search budget if you want to capture the highest intent searchers for your industry.
How To Build A Search Campaign
So you know you need Google Search Ads, where do you start? Other than hiring the best local digital agency (us), we’ve compiled a step by step guide for you to do it all on your own!
1. Establish Goals
So many people get straight into setting up keywords and ads without going through what we think is the most important step. Talking to the business. Ask very specific questions in the interview process before you set up the account. What are their goals? Do they have a very specific product or need?
The best result for the business is one that gets them the biggest return on their investment (ROI). So talk to them, or analyze the books yourself and determine which products and services are worth investing in. It should make financial sense; in the pizza example, it wouldn’t make sense to spend $20 a click for a $15 sale, but it might if you’re a new competitor in a tough market and want to gain lifetime customers.
With all this extra knowledge, you can move forward to the next step, fully confident that your campaign will lead to success.
2. Set Up Your Google Ads Account
By default, Google are going to want you to create a “Smart Campaigns” ads account, previously known as “Google AdWords Express”. We are discussing a professional, full feature Google Search Ads experience, so be sure to set up a FULL Google Ads account.
Sign Up For A Google Ads Account 
You have to use a Google Account for this, so either a gmail email address, or an email using Google Cloud. Please also make sure you have Google Tag Manager, Google My Business and Google Analytics under the same Google Account, this way we can link them all together for the best possible set up.
3. Campaign Level Set Up
Now that you have an account in Google Ads set up, and you have your KPI research completed, you can break out your account into campaigns.
If there is anything that needs to be allocated a set budget, it should have its own campaign. This typically focuses around core service areas or geographical regions, or sometimes both.
Let’s set up a campaign. Within Google Ads, click on “Campiagns” on the left menu, then click on the blue + button. Select new campaign and you’ll see this screen:
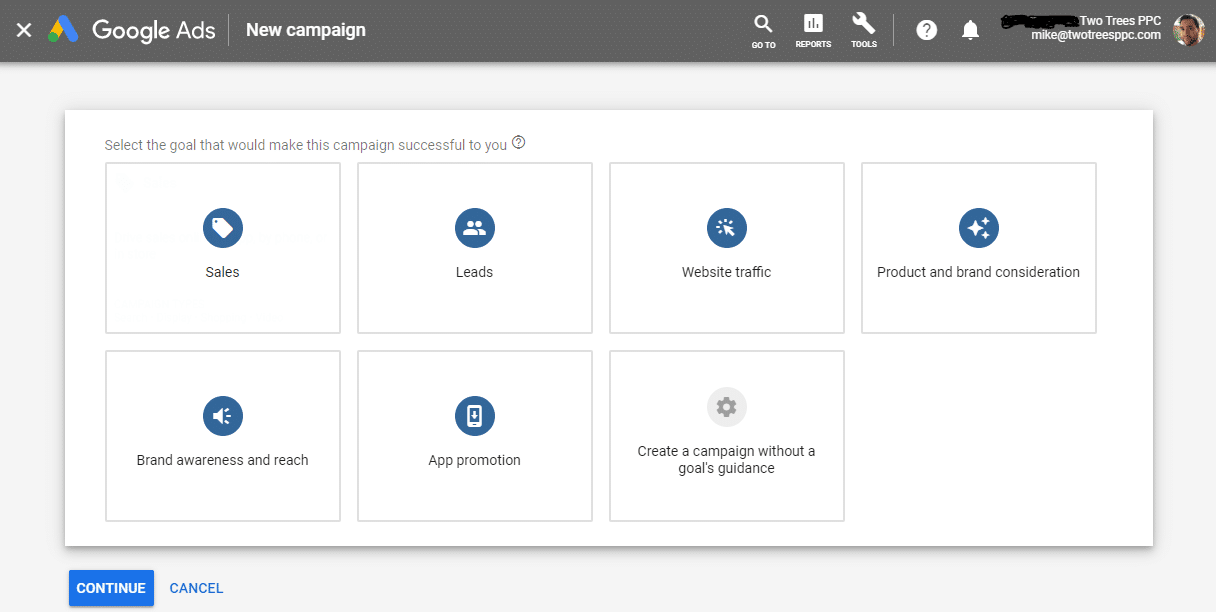
Select what makes sense for this campaign, or you can create the campaign without guidance and simply select search. Once you’ve given Google Ads the information it requested, you’ll see the campaign set up screen as follows:
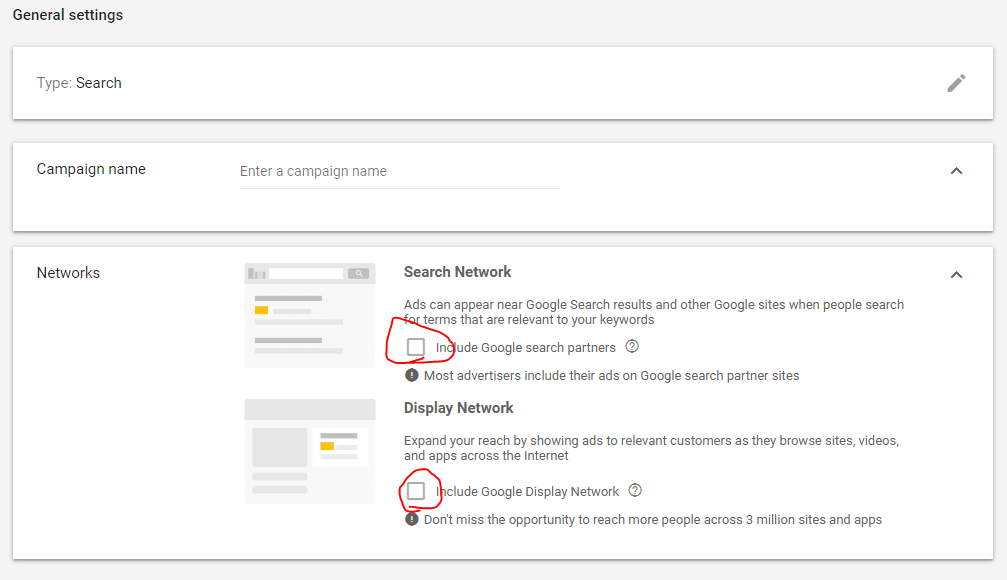
Be sure to uncheck the boxes highlighted above. Search network includes a lot of searches on third party websites and in our experience lead to less qualified searchers. You may consider running a test with this option, this option can be adjusted at anytime, the decisions you make at this stage are not permanent. Same goes with the display network, we don’t suggest ever running search ads on the display network – it doesn’t serve the purpose of what we are trying to achieve with search ads targeting those actively seeking out your product or service.
At the campaign level you will decide on what locations you want to target, this can be any geographic area you’d like. You can enter a series of ZIP codes, a Nielsen DMA, City, State, or even radius around addresses.
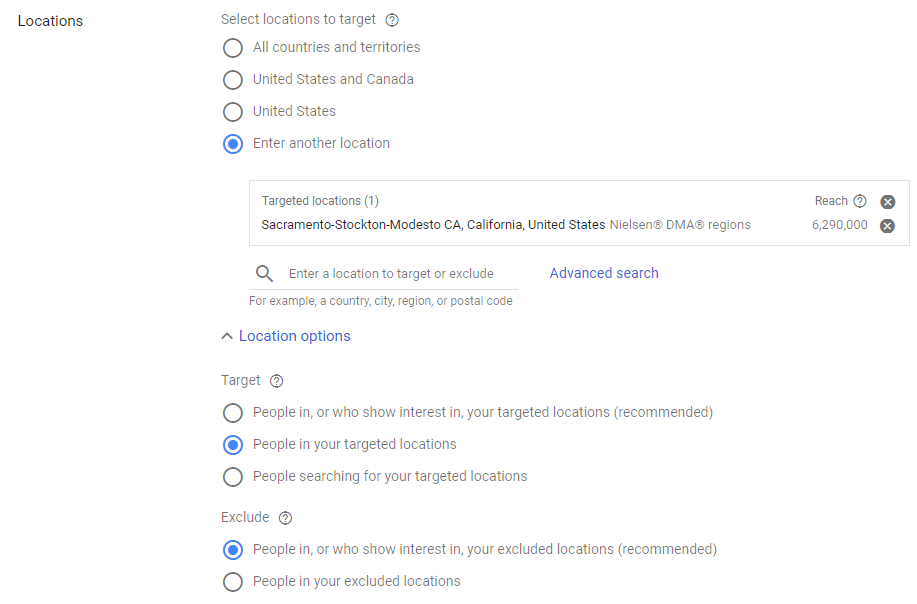
Google Ads gives us 3 options for location targeting. We often go for people in the target locations for services that are only available for locals, this means you have to physically be in the target area to see the ad. Their recommended option allows people from all over the world to see your ad if you add the geographic location to the search term. This may be a great option for people looking for a service or product on behalf of someone who does live in the target area, or if they are going to be in the area to use the product or service being offered.
Next up we have to set the budget for this campaign. Google Ads works on a daily budget, if you have a set monthly budget in mind, bear in mind also that Google can spend up to twice the amount you set each day to avoid you losing in auctions. They will however aim to stick to your average daily budget you set, but this takes time for the algorithm to work out.
You have two options on how you’d like Google to spend your money – standard or accelerated. Standard will aim to spend your daily budget evenly over time, accelerated will aggressively spend your budget until it’s depleted. If you’re a business that wants all your calls early in the day, or want maximum exposure in the mornings, go ahead and select accelerated, otherwise, keep with standard.
4. Ad Group Set Up
Now you have your basic campaign shell, you need to fill it with Ad Groups. These Ad Groups will be based around no more that 30 keywords with a tight common theme. Each Ad Group will focus around one core theme. The key here is being relevant to the searcher’s intent. Each Ad Group should answer just ONE QUESTION, this may result in a lot of ad groups, but that is ok. We do want to avoid a lot of ad groups when running with a small budget however. The system will spread the budget too thinly across your whole account, so keep your structure focused around the most important questions and answers.
The keywords are selected at the ad group level, and we suggest using the longest tail, exact match keywords as you possibly can. What this means is using highly specific, high intent keywords. These will be cheaper than broad match keywords and get you better quality clicks, but it will (and should) reduce your impressions.
Keyword planner is totally your friend in this phase of the set up. Use it to help you determine the volume of longer tail keywords in your target area. In the upper right corner, click the tools icon ![]() , then under “Planning,” click Keyword Planner. You can enter in the URL of any well index website to get an idea of the keywords that have the highest relevance. I would sort the keywords by volume, then add the most promising to your Ad Group.
, then under “Planning,” click Keyword Planner. You can enter in the URL of any well index website to get an idea of the keywords that have the highest relevance. I would sort the keywords by volume, then add the most promising to your Ad Group.
In terms of keywords, you should be thinking what the questions are for your ideal customer. What would you type into or say to Google to get it to find the best result for what you need. Those questions are your long tail keywords.
5. Ad Copy
Just as keywords in the Ad Group are your questions, the Ad Copy has to answer those questions. The problem is that you need to answer the question firmly within the character count allowed. The other challenge is that when ads are served, they can be a wide variety of sizes. We recommend using Responsive Search Ads when available. What these do are allow you to tell Google every possible headline you want for your ad, and every possible description. The system then makes the perfect fitting ad for the searcher. Results have proven a higher engagement rate with these types of ads, so we now exclusively use them.
Ads are made up of the following elements:
- Headlines – Up to 3 can show (30 character max)
- Descriptions – Up to 2 can show (90 character max)
- Path 1 – The first word after the URL (15 character max)
- Path 2 – The second word after the URL (15 character max)
- Final URL – this will be the landing page the ad goes to, the URL should match the domain for the entire ad group, ads must go to the same domain.
6. Extensions
Extensions are important and shouldn’t ever be forgotten. These make your ads stand out and on average get you a 15% greater engagement level.
You should aim to have at least 3 of the following options enabled for your ads:
Location Extensions
Linked to your Google My Business Listing, this extension pulls in the closest location to the searcher and when clicked takes them to the map
Call Extensions
Add a phone number to the ad, we recommend using a tracking number to monitor how effective your ads are. Click to call straight from the ad.
Sitelink Extensions
Link to specific pages on your website that provide further answers to searcher’s questions.
Price Extensions
Call out the price point of 3 or more items and show them directly under the ad.
Callout Extensions
Add additional text to your ads, use unique selling points like “Open 24 Hours” or “Free Delivery”. Limited to 25 characters.
Message Extensions
Have your searchers send a text directly from the ad. Requires a phone number that accepts text messages.
Structured Snippet Extensions
Showcase the quick information that searchers will want to know. Like what brands you sell or what services you offer.
Promotion Extensions
Add a tag to the bottom of the ad with a % or fixed discount, you must show this on your website too. Can add promo codes directly to the ad.
It’s important to note, Google may not show any of these extensions on your ad, you need to ensure your ad rank score is high enough to qualify. Your ad rank is calculated based upon how relevant your ad, and landing page experience is to the search term used. Which is why it is so important you think about your set up and your target audience.
7. Bid Strategy
Google Search Ads operate in an auction style for the top placement on the SERPs. Going back to the research we did in the first step, we should consider the absolute maximum cost per click that would make sense for the goal. For example, $100 for a click about a $10 pizza doesn’t necessarily make sense.
With this maximum in mind, and considering our goals, we can select a bidding strategy for each of our campaigns. We recommend setting up conversion tracking, then optimizing your bids for conversions. A conversion should be an action the user takes that signals a real intent to purchase your product or service, most often we use form submissions, calls or actual purchases as a conversion. Optimizing for conversions gives us 3 bid strategy options:
- Target CPA – We tell Google Ads how much we’d like to spend per conversion, then the algorithm uses historical campaign data to deliver your ad to the most likely searchers for conversions. If we set the target too low, or there isn’t enough conversion data to work from, this strategy will lead to a reduced number of conversions.
- Target ROAS (return-on-ad-spend) – This uses the conversion value data (so make sure that is accurate), to optimize for the more valuable conversions. We set a % of ROAS we’d like and Google optimizes for this. So if we want $1 in ad spend to result in $10 in sales, we set that as a 1000% ROAS target.
- Maximize Conversions – instead of focusing on the cost per conversion, this setting uses your total available budget to get as many conversions as possible within the target budget. It’s important that all conversions set up are valuable because the system will spend all of your budget towards getting searchers who will take the actions you want.
When we don’t have conversions set up, either because we just started, or the campaign is more about exposure than actual conversions we have the following options we recommend for bidding strategy:
- Maximize Clicks – This is the simplest way to bid, your ad will be shown to bring you the most possible clicks for your target budget.
- Manual CPC – this is the most hands on strategy and we advise to only use this if you monitor your campaign several times a day. You set the maximum bid for each ad group and can manually adjust more of your budget to go towards certain keywords.
Competitive bidding strategies can be used where you are in a highly competitive market, or you just simply want to beat our your competitor(s).
- Target Search Page Location – this bidding strategy sets your bids as high as they need to go to appear at the top of the page, or you can set it just to appear somewhere on the first page.
- Target Outranking Share – with this strategy you can select a domain to outrank in every auction, or you can select the percentage of time you want to outrank them if you are concerned about budget. This can only currently work for one domain, so pick the biggest competitor!
8. Landing Page
Where you are driving your ad to is just as important as all of the above steps. Google considers the landing page experience in it’s ranking factors. So it’s important your landing page passes the following checks:
- Fast Loading
- Secured with SSL (https)
- No redirects / popups
- Clear call to action at the top
- A fixed header with contact details clearly displayed
- One core offer / theme
- Easy way to opt in / leave details
We like to use a professional landing page provider to ensure the above requirements are always met, also the reporting and analytics need to be integrated, and our choice of provider has the best tracking available on the market.
Measuring & Determining Success
So now you have a fully functioning Google Search Ads campaign set up. But how do you know it is successful and optimized to get you the best return on your investment.
The most obvious sign of success, and all that really matters is your ROI, return on investment. If you spend $2,000 on ads, you should certainly be generating more than $2,000 in new sales.
We see a lot of agencies and “gurus” talk about impression share, click through rate and cost per click as their primary indicators of success; although these are important to track and keep an eye on, they alone do not determine the success of the campaign.
At our agency, we produce Google Data Studio dashboards for our clients, which allows them to constantly check on their vital stats at any time. The key things we want to monitor, other than conversions and cost per conversion, are Click Share, Cost Per Click, Click Through Rate and Conversion Rate.
You now have everything you need to set up and monitor a successful Google Search Ads campaign. But if you want to speak to a real human being, we are here to talk you through the process and can do as much or as little for you as you need. Read more about how to increase conversions!
